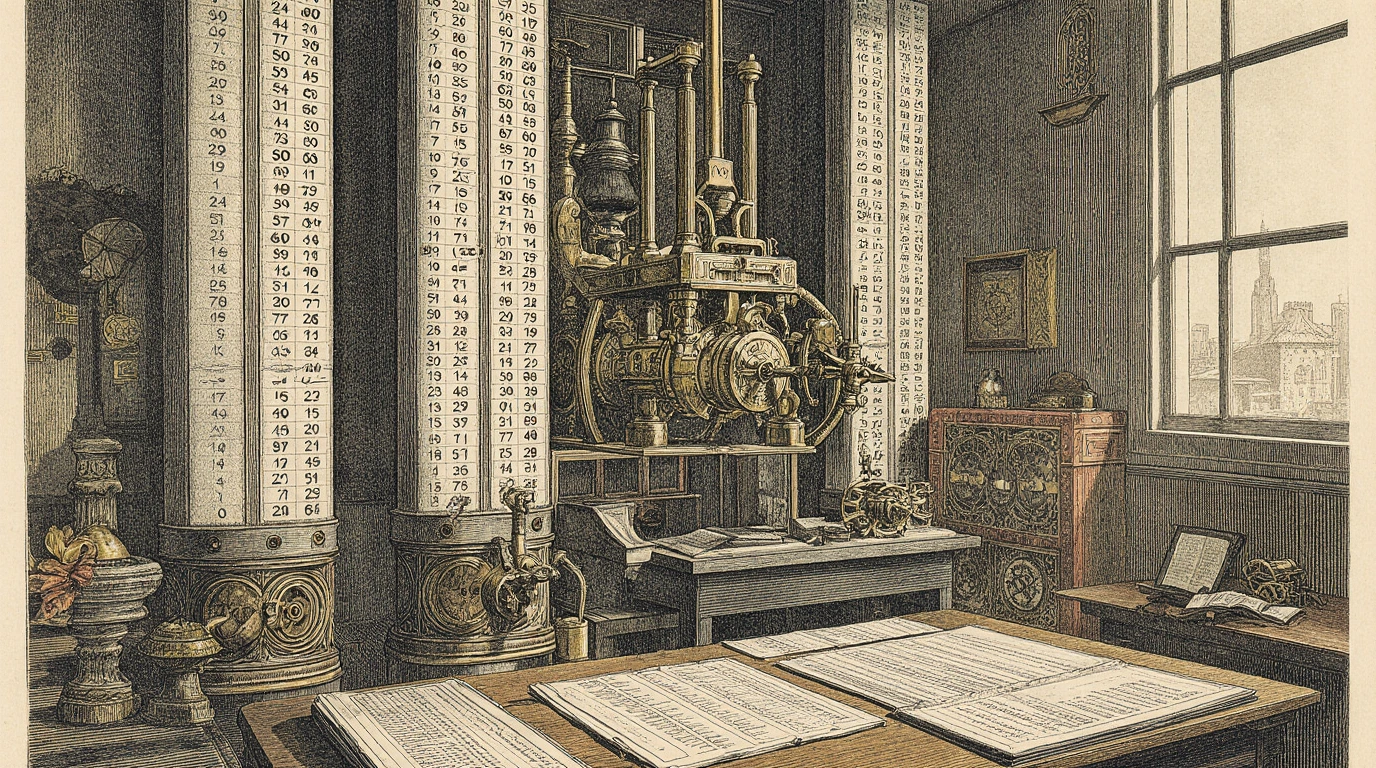
The Difference Engine occupies a distinctive place in the history of computing because it represents a moment when calculation was first entrusted to machinery rather than human effort. Conceived in the early nineteenth century, the Difference Engine was designed to eliminate errors in mathematical tables by automating repetitive numerical work. Although later developments would move far beyond its capabilities, the Difference Engine remains a foundational step in understanding how computation began to shift from theory into mechanism.
This article forms part of the wider Ada Lovelace cluster on Walkeropedia. For an overview of how the Difference Engine fits into that broader intellectual landscape, see the Ada Lovelace Cluster Home.
What Is a Difference Engine?
A common question when encountering early mechanical computation is simply: what is a difference engine? In essence, it is a specialised calculating machine designed to compute polynomial functions using the mathematical method of finite differences. By relying on repeated addition rather than multiplication or division, the machine could generate accurate numerical tables automatically.
Vacant Space 1
Space Reserved for possible future development.
Unlike later computing devices, the machine was not programmable in the modern sense. It followed a fixed procedure determined by its construction. This limitation, however, was also its strength: the machine was optimised for precision and reliability in a specific class of calculations.
Understanding the difference engine requires recognising the problem it was meant to solve. In the early nineteenth century, mathematical tables were produced by hand, and errors were common. Even a single mistake could have serious consequences in navigation, engineering, or astronomy. The machine promised consistency at a time when accuracy mattered deeply.

Babbage’s Difference Engine and Its Design
The origins of Babbage’s Difference Engine lie in Charles Babbage’s frustration with human error. As a mathematician and inventor, Babbage believed that machines could outperform people at repetitive tasks if designed correctly. His solution was a purely mechanical system capable of performing additions with exact regularity.
The difference engine design was both elegant and ambitious. It consisted of vertical columns of numbered wheels, each representing a decimal digit. Through a carefully choreographed sequence of rotations and carries, the machine could calculate successive values of a polynomial function. Once set up, the engine would proceed step by step, printing results without further intervention.
This approach made the Charles Babbage difference engine fundamentally different from later computing concepts. It was not intended to manipulate symbols or follow changing instructions. Instead, it embodied a single mathematical idea, implemented with extraordinary mechanical precision. For a broader view of Babbage’s ambitions, see Charles Babbage – The Visionary Engineer.

Difference Engine History in the Nineteenth Century
The difference engine history is inseparable from the scientific culture of its time. Early nineteenth-century Britain placed great value on practical mathematics, particularly in navigation, surveying, and engineering. Accurate tables were essential tools, and governments were willing to fund projects that promised reliability.
Initial support for Babbage’s work reflected this environment. Yet the project soon encountered difficulties. The engineering tolerances required were extreme, and the costs escalated. Disagreements between Babbage and his chief engineer further slowed progress. As a result, the original machine was never completed during Babbage’s lifetime.
Despite this setback, the idea did not vanish. The intellectual legacy of the machine continued to influence later thinking about automation and calculation. The broader scientific backdrop to these developments is explored in Victorian Science & Society and 19th-Century Science.
From Fixed Calculation to Programmability
While the machine was limited to a single method, its existence paved the way for more ambitious ideas. The contrast between the Difference Engine and the later Analytical Engine is particularly revealing. Where one followed a fixed procedure, the other aimed to follow instructions.
This distinction explains why discussions of symbolic processing and abstract logic emerge so naturally from Babbage’s later work. The machine demonstrated that mechanical calculation was possible; the next step was to ask whether machines could manipulate symbols rather than numbers alone. That conceptual leap is explored in Symbolic Processing: Lovelace and Babbage and Logic and Algorithms: Babbage and Lovelace.
Although the Difference Engine itself did not belong to the early history of programming, it helped create the conditions in which programming could be imagined. Its place alongside later developments is discussed further in Early History of Programming.

Scientific Networks and Wider Influence
Babbage did not work in isolation. His ideas circulated within a dense network of nineteenth-century scientists, engineers, and thinkers. Figures such as Michael Faraday exemplified the experimental spirit of the age, even when their work lay in different domains.
The presence of Ada Lovelace within this intellectual milieu also mattered. Although her most famous contributions relate to the Analytical Engine, her engagement with Babbage’s earlier work forms part of the broader story of women’s participation in science and technology. This context is explored in Women in Science & Technology History.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
The enduring importance of the Difference Engine lies in what it revealed about the relationship between mathematics and machinery. By translating a single mathematical method into physical form, the machine demonstrated that calculation could be automated with remarkable precision.
Seen in context, the difference engine was never intended to be a universal solution. Its limitations were clear even to its creator. Yet within those limits, it represented a decisive step forward. The difference engine history shows how practical needs, scientific ambition, and mechanical ingenuity combined to reshape expectations about what machines could do.
By examining Babbage’s Difference Engine, we gain insight into a transitional moment: a world moving from hand-crafted calculation toward the programmable systems that would follow. The Difference Engine did not end the story of computation, but it ensured that the story could continue.
External reference:
Encyclopaedia Britannica – Difference Engine
https://www.britannica.com/technology/Difference-Engine
“Save the trees, they allow us to breathe.”
– Stephenism
🎵 Soul from the Solo Blogger — Tunes from Túrail.